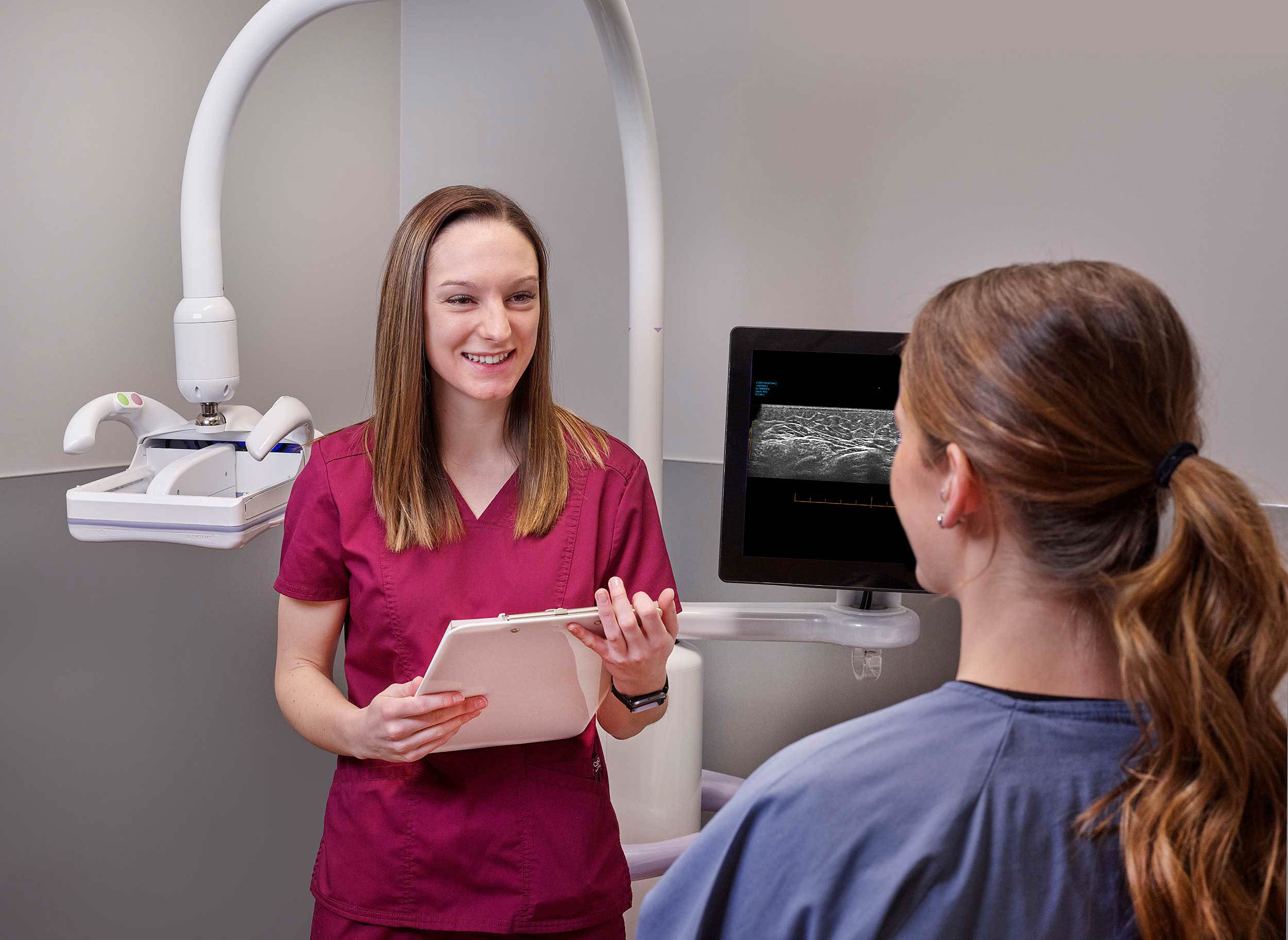
Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)
Automated Breast Imaging (ABUS) is a quick exam that uses sound waves and a wide transducer to scan the entire breast and create hundreds of 3D images of the tissue. The resulting 3D images can be a useful reference point for radiologists during future visits, comparing tissue and composition.
During the appointment, your technologist will ask you to lie on the exam table and will apply a warm, water-based gel or cream over your breast. A wide rectangular transducer will be pressed against your entire breast, automatically scanning the area with minimal discomfort.
Hand-Held Ultrasound (HHUS)
Hand-Held Ultrasound (HHUS) is an essential tool in modern breast cancer screening, particularly for individuals with heterogeneously or extremely dense breast tissue (classification C or D). HHUS involves the use of a portable ultrasound device operated by a highly trained technologist who scans both breasts entirely.
During a Hand-Held Ultrasound, your technologist will apply a warm, water-based gel directly on your skin and use a small transducer to bilaterally screen both breasts entirely. Compared to an ABUS, the pressure from an HHUS is more targeted, as the technologist moves the transducer across both breasts.
HHUS provides several benefits that make it an excellent option for supplemental screening, including:
-
- Increased sensitivity in detecting cancer in dense breasts.
-
- Doppler imaging to view vascularity in the tissue, which can help in diagnosis.
ABUS vs. HHUS
Both forms of supplemental imaging have been proven to increase breast cancer detection significantly. From a patient’s perspective, the main differences between ABUS and HHUS are:
-
- The pressure from ABUS is applied across the entire breast at once. HHUS is a more targeted pressure that moves around the breast throughout the exam.
-
- The ABUS transducer may interfere with patients who have pacemakers or similar devices, potentially leaving HHUS as a more viable alternative.
-
- ABUS exams take approximately 15 minutes to complete. Conversely, HHUS can last anywhere from 5 to 30 minutes, depending on the patient and their tissue composition. More often, HHUS exams tend to take longer than ABUS.
Diagnostic Ultrasound Exams
Following your screening mammogram, your radiologist or your healthcare practitioner may want to look more closely at a targeted area in your breast tissue with a diagnostic breast ultrasound. Your practitioner may also request a diagnostic ultrasound if you have a lump or you are having pain and tenderness that is not usual for you.
During a diagnostic ultrasound exam, your technologist will place a warm, water-based gel directly on your skin and then use a small transducer or probe to pass over the area. The transducer transmits high-frequency sound waves through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back, and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image.